Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression levels of the serum transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) CXC type chemokine ligand 13 (CXCL13) in primary Sjogren’s syndrome (pSS) patients and its correlation with disease severity.
Method
Thirty patients with pSS admitted to Nan**g Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital of Nan**g University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from January 2021 to December 2022 were included as the pSS group, while 30 patients who underwent physical examination during the same period were included as the control group. The levels of TGF-β1 and CXCL13 were detected. The diagnostic value of TGF-β1 and CXCL13 for pSS was analyzed. Detection of serum TGF-β1 and CXCL13 levels in pSS patients with different disease activities and lip gland pathological grading of pSS was done. We compared the correlation between TGF-β1 and CXCL13 levels and disease activity and labial gland pathological grading in pSS patients.
Result
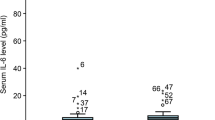
The TGF-β1 and CXCL13 levels in the pSS group were higher than those in the control group. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) for TGF-β1 and CXCL13 diagnosis of pSS was 0.790 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.720~0.861) and 0.838 (95% CI: 0.778~0.898), respectively. The serum TGF-β1 and CXCL13 levels of pSS patients significantly increase with the increase of disease activity and lip gland pathological grading. The TGF-β1 and CXCL13 levels in pSS patients were positively correlated with disease activity and lip gland pathological grading.
Conclusion
The levels of TGF-β1 and CXCL13 in pSS patients were increased, and it was closely related to disease activity and lip gland pathological grading, which can be used as an effective indicator for the diagnosis of pSS.
Key Points • The TGF-β1 and CXCL13 levels in the pSS group were higher than those in the control group. • The TGF-β1 and CXCL13 levels in pSS patients were positively correlated with disease activity and lip gland pathological grading. • TGF-β1 and CXCL13 can be used as an effective indicator for the diagnosis of pSS. |





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomiak C, Dorner T (2006) Sjogren’s syndrome. Current aspects from a rheumatological point of view. Z Rheumatol 65:505–517
Qin B, Wang J, Yang Z et al (2015) Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1983–1989
Westhoff G, Zink A (2010) Epidemiology of primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Z Rheumatol 69:41–49
Margherita S, Roberto T, Domenico R et al (2020) IL-6 contributes to the TGF-β1-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human salivary gland epithelial cells. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 68(5):27
Chung YL et al (2023) The wound-healing activity of PEDOT-PSS in animals. Int J Mol Sci 24(16):12539
Brito-Zeron P, Theander E, Baldini C et al (2016) Early diagnosis of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: EULAR-SS task force clinical recommendations. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 12:137–156
Fox PC, Bowman SJ, Segal B et al (2008) Oral involvement in primary Sjögren syndrome. J Am Dent Assoc 139:1592–1601
Bron AJ, Tomlinson A, Foulks GN et al (2014) Rethinking dry eye disease: a perspective on clinical implications. Ocul Surf 12:1–31
Villa A, Abati S (2011) Risk factors and symptoms associated with xerostomia: a cross-sectional study. Aust Dent J 56:290–295
Cornec D, Saraux A, Jousse-Joulin S et al (2015) The differential diagnosis of dry eyes, dry mouth, and parotidomegaly: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 49:278–287
Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zeron P, Solans R et al (2014) Systemic involvement in primary Sjögren’s syndrome evaluated by the EULAR-SS disease activity index: analysis of 921 Spanish patients (GEAS-SS Registry). Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:321–331
Nishishinya MB, Pereda CA, Munoz-Fernandez S et al (2015) Identification of lymphoma predictors in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 35:17–26
Theander E, Vasaitis L, Baecklund E et al (2011) Lymphoid organisation in labial salivary gland biopsies is a possible predictor for the development of malignant lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1363–1368
Flament T, Bigot A, Chaigne B, Henique H, Diot E, Marchand-Adam S (2016) Pulmonary manifestations of Sjögren’s syndrome. Eur Respir Rev 25:110–123
Evans R, Zdebik A, Ciurtin C, Walsh SB (2015) Renal involvement in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 549:1541–1548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Xu, C., Zhu, Y. et al. Clinical significance of the expression levels of serum transforming growth factor-β and CXC type chemokine ligand 13 in primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients. Clin Rheumatol 42, 3283–3288 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06783-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06783-6