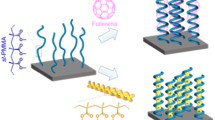
Abstract
Polymer brushes are special structures that can be described as polymer chains tethered to another polymer chain or to the surface of planar, cylindrical, or spherical matrix. Tremendous potential applications of polymer brushes have been explored such as in drug delivery, antifouling coating, and enhance oil recovery (EOR). Herein, combining the “grafting to” and “grafting from” techniques, we present a facile and scalable method to obtain spherical polymer brushes utilizing a rational designed difunctional ligand. The difunctional ligand allows for the generation of polymer colloidal core along with the growth of polymer chains in situ at the surface simultaneously. By this strategy, a well-defined spherical polymer brushes with core–shell morphology were formed in a high yield (95%). Benefiting from the difunctional ligand, the usage of emulsifier for emulsion polymerization was adequately reduced. Furthermore, the obtained polymer brushes exhibit excellent surface and interfacial activity. Oil–water interfacial tension reduced approximately 9 mN/m at extremely low concentration (1.0 ppm). Meanwhile, the obtained polymer brushes can stabilize O/W emulsion more effectively than the unmodified counterparts. Additionally, the swelling behavior of the well-defined polymer brushes could be well controlled by cross-link degree. This strategy will provide a new avenue for scalable synthesis of polymer brush–based functional materials for industrial applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Advincula, Brittain JW, Caster KC, Rühe J RC (2004) Polymer Brushes. Wiley-VCH, Weiheim
Azzaroni O (2012) Polymer brushes here, there, and everywhere: recent advances in their practical applications and emerging opportunities in multiple research fields. J. Polym. Sci. Part a: Polym Chem 50:3225–3258. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.26119
Barbey R, Lavanant L, Paripovic D, Schüwer N, Sugnaux C, Tugulu S, Klok H-A (2009) Polymer Brushes via surface-initiated controlled radical polymerization: synthesis, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem Rev 109:5437–5527. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900045a
Benetti EM (2018) Quasi-3D-structured interfaces by polymer brushes. Macromol Rapid Commun 39:e1800189. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201800189
Blundell RK, Licence P (2014) Quaternary ammonium and phosphonium based ionic liquids: a comparison of common anions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:15278–15288. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp01901f
Caleb JR, Stephen GB (2021) New methods in polymer brush synthesis: non-vinyl-based semiflexible and rigid-rod polymer brushes. Prog Polym Sci 114:101361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2021.101361
Chandran S, Begam N, Padmanabhan V, Basu JK (2014) Confinement enhances dispersion in nanoparticle-polymer blend films. Nat Commun 5:3697. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4697
Chen T, Amin I, Jordan R (2012) Patterned polymer brushes. Chem Soc Rev 41:3280–3296. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs15225h
Chen W-L, Cordero R, Tran H, Ober CK (2017) 50th Anniversary Perspective: Polymer brushes: novel surfaces for future materials. Macromolecules 50:4089–4113. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.7b00450
Edmondson S, Osborne VL, Huck WTS (2004) Polymer brushes via surface-initiated polymerizations. Chem Soc Rev 33:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1039/b210143m
Feng C, Huang X (2018) Polymer Brushes: Efficient Synthesis and Applications. Acc Chem Res 51:2314–2323. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00307
Glaser N, Adams DJ, Böker A, Krausch G (2006) Janus particles at liquid−liquid interfaces. Langmuir 22:5227–5229. https://doi.org/10.1021/la060693i
Goldmann AS, Boase NRB, Michalek L, Blinco JP, Welle A, Barner-Kowollik C (2019) Adaptable and reprogrammable surfaces. Adv Mater 31:1902665. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201902665
Hu L, Hao Q, Wang L, Cui Z, Fu P, Liu M, Qiao X, Pang X (2021) The in situ “grafting from” approach for the synthesis of polymer brushes on upconversion nanoparticles via NIR-mediated RAFT polymerization. Polym Chem 12:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0py01550d
Kim M, Schmitt S, Choi J, Krutty J, Gopalan P (2015) From self-assembled monolayers to coatings: advances in the synthesis and nanobio applications of polymer brushes. Polymers 7:1346–1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7071346
Lee W, Jung JW (2016) High performance polymer solar cells employing a low-temperature solution-processed organic–inorganic hybrid electron transport layer. J Mater Chem a 4:16612–16618. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta06911h
Li Z, Lu J, Li SD, Qin SH, Qin YM (2012) Orderly ultrathin films based on perylene/poly(N-vinyl carbazole) assembled with layered double hydroxide nanosheets: 2D fluorescence resonance energy transfer and reversible fluorescence response for volatile organic compounds. Adv Mater 24:6053–6057. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201203040
Li Y, Jian Z, Lang M, Zhang C, Huang X (2016) Covalently Functionalized graphene by radical polymers for graphene-based high-performance cathode materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:17352–17359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b05271
Ling D, Hackett MJ, Hyeon T (2014) Surface ligands in synthesis, modification, assembly and biomedical applications of nanoparticles. Nano Today 9:457–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2014.06.005
Liu Y, Hou W, Zhao H (2020) Synthesis of Y-shaped polymer brushes on silica particles and hierarchical surface structures fabricated by the coassembly approach. Macromolecules 53:5001–5014. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00397
Luo D, Wang F, Zhu J, Cao F, Liu Y, Li X, Willson RC, Yang Z, Chu C-W, Ren Z (2016) Nanofluid of graphene-based amphiphilic Janus nanosheets for tertiary or enhanced oil recovery: high performance at low concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:7711–7716. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1608135113
Mei S, Li CY (2018) Terraced and smooth gradient polymer brushes via a polymer single-crystal assisted grafting-to method. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:15758–15761. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201809915
Milner ST (1991) Polymer Brushes. Science 251:905–914. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.251.4996.905
Nie H, Zhang C, Liu Y, He A (2016) Synthesis of janus rubber hybrid particles and interfacial behavior. Macromolecules 49:2238–2244. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.6b00159
Niu Z, Yang Z, Hu Z, Lu Y, Han CC (2003) Polyaniline–silica composite conductive capsules and hollow spheres. Adv Funct Mater 13:949–954. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200304460
Que Y, Liu Y, Tan W, Feng C, Shi P, Li Y, **aoyu H (2016) Enhancing photodynamic therapy efficacy by using fluorinated nanoplatform. ACS Macro Lett 5:168–173. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.5b00935
Tadros T (2009) Polymeric surfactants in disperse systems. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 147–148:281–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2008.10.005
Wang G, Wang K, Wang Y (2018) Synthesis of amphiphilic fluorinated Janus particles with applications in stabilizing surfactant-free foams. Particuology 41:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2017.12.006
Wang Z, Liu T, Zhao Y, Lee J, Wei Q, Yan J, Li S, Olszewski M, Yin R, Zhai Y, Bockstaller MR, Matyjaszewski K (2019) Synthesis of gradient copolymer grafted particle brushes by ATRP. Macromolecules 52:9466–9475. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02157
**e G, Krys P, Tilton RD, Matyjaszewski K (2017) Heterografted molecular brushes as stabilizers for water-in-oil emulsions. Macromolecules 50:2942–2950. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.7b00006
**ong Y, Liu J, Wang Y, Wang H, Wang R (2012) One-step synthesis of thermosensitive nanogels based on highly cross-linked poly(ionic liquid)s. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:9114–9118. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201202957
Xu B, Feng C, Hu J, Shi P, Gu G, Wang L, Huang X (2016) Spin-casting polymer brush films for stimuli-responsive and anti-fouling surfaces. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:6685–6692. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b12820
Xu B, Feng C, Huang X (2017a) A versatile platform for precise synthesis of asymmetric molecular brush in one shot. Nat Commun 8:333. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00365-2
Xu B, Liu Y, Sun X, Hu J, Shi P, Huang X (2017b) Semifluorinated synergistic nonfouling/fouling-release surface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:16517–16523. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03258
Yan J, Bockstaller MR, Matyjaszewski K (2020) Brush-modified materials: control of molecular architecture, assembly behavior, properties and applications. Prog Polym Sci 100:101180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2019.101180
Yuan FL, Wang ZB, Li XH, Li YC, Tan ZA, Fan LZ, Yang SH (2017) Bright multicolor bandgap fluorescent carbon quantum dots for electroluminescent light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 29:6. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201604436
Zhang R, Leiviskä T (2020) Surface modification of pine bark with quaternary ammonium groups and its use for vanadium removal. Chem Eng J 385:123967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123967
Zhang M, Müller AHE (2005) Cylindrical polymer brushes. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 43:3461–3481. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.20900
Zhang C, Ding S, Li J, Xu H, Sun L, Wei W, Li C, Liu J, Qu X, Lu Y, Yang Z (2008) Interpenetration network (IPN) assisted transcription of polymeric hollow spheres: a general approach towards composite hollow spheres. Polymer 49:3098–3102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.04.060
Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Zhao B, Huang Y, **ong J, Cai P, Xue X, Zhang J, Tan S (2018) Polymer with a 3D conductive network: a thickness-insensitive electron transport layer for inverted polymer solar cells. J Mater Chem a 6:12969–12973. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta01352g
Zhao B, Deng JP (2017) Emulsion polymerization of acetylenics for constructing optically active helical polymer nanoparticles. Polym Rev 57:119–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2015.1136642
Zhou X, Liu X, **e Z, Zheng Z (2011) 3D-patterned polymer brush surfaces. Nanoscale 3:4929–4939. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1nr11238d
Zoppe JO, Ataman NC, Mocny P, Wang J, Moraes J, Klok H-A (2017) Surface-initiated controlled radical polymerization: state-of-the-art, opportunities, and challenges in surface and interface engineering with polymer brushes. Chem Rev 117:1105–1318. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00314
Funding
This work was supported by the Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (2020YJ0363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Consent for publication
I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was an original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part, in any language.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., Duan, M., Fang, S. et al. Difunctional ligands assist a facile scalable strategy for the synthesis of spherical polymer brushes. J Nanopart Res 24, 29 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05419-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05419-1