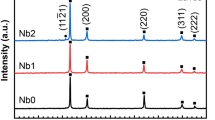
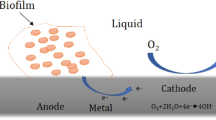
Abstract
Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) is a bacterium that can cause microbial corrosion. SRB often leads to corrosion and perforation of oil and gas pipelines. Cathodic polarization is usually used for pipe external corrosion protection, while cathodic polarization may influence the growth and reproduction of SRB on the pipe wall. Based on 14-day electrochemical experiments and morphological characterization of corrosion product, SRB corrosion on L360N under different cathodic polarization potentials was analyzed. Under the action of cathodic protection potential, − 0.85 VSCE stimulated SRB metabolism and accelerated corrosion due to a large amount of electron supply. At − 0.95 VSCE and below, the SRB adsorption process was interrupted, which could play a protective role. The conclusions of this study could provide basic guidance for the corrosion prevention of L360N steel with SRB corrosion environment and reduce the economic losses caused by microbial corrosion.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.L. Enze Zhoua, C. Yang, J. Wang, D. Xua, D. Zhang, and G. Tingyue, Accelerated Corrosion of 2304 Duplex Stainless Steel by Marine Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2018, 127, p 1–9.
D. Wang, J. Liu, R. Jia, W. Dou, S. Kumseranee, S. Punpruk, X. Li, and T. Gu, Distinguishing two Different Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC) Mechanisms using an Electron Mediator and Hydrogen Evolution Detection, Corros. Sci., 2020, 177, p 108993.
H. Tian, X. Wang, Z. Cui, Q. Lu, L. Wang, L. Lei, Y. Li, and D. Zhang, Electrochemical Corrosion, Hydrogen Permeation and Stress Corrosion Cracking Behavior of E690 Steel in Thiosulfate-Containing Artificial Seawater, Corros. Sci., 2018, 144, p 145–162.
Y. Li, D. Xu, C. Chen, X. Li, R. Jia, D. Zhang, W. Sand, F. Wang, and T. Gu, Anaerobic Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Mechanisms Interpreted using Bioenergetics and Bioelectrochemistry: A Review, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34(10), p 1713–1718.
M. Lv and M. Du, A Review: Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and the Effect of Cathodic Polarization on Typical Bacteria, Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol., 2018, 17(3), p 431–446.
Y.G.K.S.Y. Li, K.S. Jeon, Y.T. Kho, and T. Kang, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Carbon Steel Exposed to Anaerobic Soil, Corros. Eng. Sect., 2001, 57(9), p 815–828.
H. Liu and Y.F. Cheng, Mechanistic Aspects of Microbially Influenced Corrosion of X52 Pipeline Steel in a Thin Layer of Soil Solution Containing Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria under Various Gassing Conditions, Corros. Sci., 2018, 133, p 178–189.
W. Dou, J. Liu, W. Cai, D. Wang, R. Jia, S. Chen, and T. Gu, Electrochemical Investigation of Increased Carbon Steel Corrosion via Extracellular Electron Transfer by a Sulfate Reducing Bacterium under Carbon Source Starvation, Corros. Sci., 2019, 150, p 258–267.
R. Jia, D. Yang, J. Xu, D. Xu, and T. Gu, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of C1018 Carbon Steel by Nitrate Reducing Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm under Organic Carbon Starvation, Corros. Sci., 2017, 127, p 1–9.
L. Wang, J. **n, L. Cheng, K. Zhao, B. Sun, J. Li, X. Wang, and Z. Cui, Influence of Inclusions on Initiation of Pitting Corrosion and Stress Corrosion Cracking of X70 Steel in Near-neutral pH Environment, Corros. Sci., 2019, 147, p 108–127.
C.A. Kuhr and L.S. Van der Vlugt, The Graphitization of Cast Iron as an Electrobiochemical Process in Anaerobic Soils, Water, 1934, 18(16), p 147–165.
D. Blackwood, An Electrochemist Perspective of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion, Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 2018, 1(1), p 59–76.
P. Zhang, D. Xu, Y. Li, K. Yang, and T. Gu, Electron Mediators Accelerate the Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel by the Desulfovibrio Vulgaris Biofilm, Bioelectrochemistry, 2015, 101, p 14–21.
D. Xu, Y. Li, and T. Gu, Mechanistic Modeling of Biocorrosion Caused by Biofilms of Sulfate Reducing Bacteria and Acid Producing Bacteria, Bioelectrochemistry, 2016, 110, p 52–58.
L. Chen, B. Wei, and X. Xu, Effect of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria (SRB) on the Corrosion of Buried Pipe Steel in Acidic Soil Solution, Coatings, 2021, 11(6), p 625.
R. Jia, J.L. Tan, P. **, D.J. Blackwood, D. Xu, and T. Gu, Effects of Biogenic H2S on the Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of C1018 Carbon Steel by Sulfate Reducing Desulfovibrio Vulgaris Biofilm, Corros. Sci., 2018, 130, p 1–11.
X. Jiang, Q. Zhang, D. Qu, K. Xu, and X. Song, Corrosion Behavior of L360 N and L415 N Mild Steel in a Shale Gas Gathering Environment–Laboratory and On-site Studies, J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng., 2020, 82, p 103492.
H. Liu and Y. Frank Cheng, Mechanism of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of X52 Pipeline Steel in a Wet Soil Containing Sulfate-Reduced Bacteria, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 253, p 368–378.
F. Guan, X. Zhai, J. Duan, M. Zhang, and B. Hou, Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Behavior of High Strength Steel EQ70 under Cathodic Polarization, PLoS ONE, 2016, 11(9), p e0162315.
M. Shiibashi, X. Deng, W. Miran, and A. Okamoto, Mechanism of Anaerobic Microbial Corrosion Suppression by Mild Negative Cathodic Polarization on Carbon Steel, Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett., 2020, 7(9), p 690–694.
G.Z.-. Olivares, G.M. Mejia, G.G.C.R.G. Esquivel, I.G. Lopez, C.M. Ulloa-Ochoa, F.R. Dabur, Sulfate Reducing Bacteria Influence on the Cathodic Protection of Pipelines That Transport Hydrocarbons, Nace Corrosion ed., OnePetro, 2003
M. Lv, X. Li, and M. Du, The Effect of Cathodic Polarization on the Corrosion Behavior of X65 Steel in Seawater Containing Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Mater. Corros., 2020, 71(12), p 2038–2051.
D. Wang, F. **e, M. Wu, D. Sun, X. Li, and J. Ju, The Effect of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on Hydrogen Permeation of X80 Steel under Cathodic Protection Potential, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(44), p 27206–27213.
S. Permeh, K. Lau, B. Tansel, and M. Duncan, Surface Conditions for Microcosm Development and Proliferation of SRB on Steel with Cathodic Corrosion Protection, Construct. Build. Mater., 2020, 243, p 118209.
L. Kexi, Q. Min, H. Guoxi, Y. Na, and Z. Shijian, Study on Corrosion Mechanism and the Risk of the Shale Gas Gathering Pipelines, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2021, 128, p 105622.
X. Song, Y. Yang, D. Yu, G. Lan, Z. Wang, and X. Mou, Studies on the Impact of Fluid Flow on the Microbial Corrosion Behavior of Product Oil Pipelines, J. Petrol. Sci. Eng., 2016, 146, p 803–812.
K. Liao, F. Zhou, X. Song, Y. Wang, S. Zhao, J. Liang, L. Chen, and G. He, Synergistic Effect of O2 and H2S on the Corrosion Behavior of N80 Steel in a Simulated High-Pressure Flue Gas Injection System, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29(1), p 155–166.
D. Xu and T. Gu, Carbon Source Starvation Triggered More Aggressive Corrosion Against Carbon Steel by the Desulfovibrio Vulgaris Biofilm, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2014, 91, p 74–81.
L. Chen, J. Hu, X. Zhong, Q. Zhang, Y. Zheng, Z. Zhang, and D. Zeng, Corrosion Behaviors of Q345R Steel at the Initial Stage in an Oxygen-Containing Aqueous Environment: Experiment and Modeling, Materials, 2018, 11(8), p 1462.
H. Liu, C. Fu, T. Gu, G. Zhang, Y. Lv, H. Wang, and H. Liu, Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in the Presence of Sulfate Reducing Bacteria and Iron Oxidizing Bacteria Cultured in Oilfield Produced Water, Corros. Sci., 2015, 100, p 484–495.
F. Guan, X. Zhai, J. Duan, J. Zhang, K. Li, and B. Hou, Influence of Sulfate-reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Behavior of 5052 Aluminum Alloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, 316, p 171–179.
T. Gu, R. Jia, T. Unsal, and D. Xu, Toward a Better Understanding of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Caused by Sulfate Reducing Bacteria, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 35(4), p 631–636.
H. Yi, K.P. Nevin, B.C. Kim, A.E. Franks, A. Klimes, L.M. Tender, and D.R. Lovley, Selection of a Variant of Geobacter Sulfurreducens with Enhanced Capacity for Current Production in Microbial Fuel Cells, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2009, 24(12), p 3498–3503.
P. Refait, M. Jeannin, R. Sabot, H. Antony, and S. Pineau, Electrochemical Formation and Transformation of Corrosion Products on Carbon Steel under Cathodic Protection in Seawater, Corros. Sci., 2013, 71, p 32–36.
D. Starosvetsky, J. Starosvetsky, R. Armon, and Y. Ein-Eli, A Peculiar Cathodic Process during Iron and Steel Corrosion in Sulfate Reducing Bacteria (SRB) Media, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(4), p 1536–1540.
A. Jerzy Łabanowski and A. Świerczyńska, Effect of Microstructure on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel, Polish Marit. Res., 2017, 21(84), p 108–112.
R. Jia, D. Yang, D. Xu, and T. Gu, Carbon Steel Biocorrosion at 80 °C by a Thermophilic Sulfate Reducing Archaeon Biofilm Provides Evidence for its Utilization of Elemental Iron as Electron Donor Through Extracellular Electron Transfer, Corros. Sci., 2018, 145, p 47–54.
A.A. Thompson, J.L. Wood, E.A. Palombo, W.K. Green, and S.A. Wade, From Laboratory Tests to Field Trials: A Review of Cathodic Protection and Microbially Influenced Corrosion, Biofouling, 2022, 38(3), p 298–320.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 52174062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, G., Qin, M., Liao, K. et al. Corrosion Behavior of L360N Steel in the Presence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria under Three Cathodic Potentials. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08281-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08281-x