Abstract
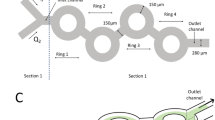
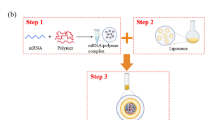
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as highly effective delivery systems for nucleic acid-based therapeutics. However, the broad clinical translation of LNP-based drugs is hampered by the lack of robust and scalable synthesis techniques that can consistently produce formulations from early development to clinical application. In this work, we proposed a method to achieve scalable synthesis of LNPs by scaling inertial microfluidic mixers isometrically in three dimensions. Moreover, a theoretical predictive method, which controls the mixing time to be equal across different chips, is developed to ensure consistent particle size and size distribution of the synthesized LNPs. LNPs loaded with small interfering RNA (siRNA) were synthesized at different flow rates, exhibiting consistent physical properties, including particle size, size distribution and encapsulation efficiency. This work provides a practical approach for scalable synthesis of LNPs consistently, offering the potential to accelerate the transition of nucleic acid drug development into clinical application.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siavashy, S.; Soltani, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Landi, B.; Mehmanparast, H.; Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh, F. A comprehensive review of one decade of microfluidic platforms applications in synthesis of enhanced carriers utilized in controlled drug delivery. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101615.
Shepherd, S. J.; Issadore, D.; Mitchell, M. J. Microfluidic formulation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2021, 274, 120826.
Bendre, A.; Bhat, M. P.; Lee, K. H.; Altalhi, T.; Alruqi, M. A.; Kurkuri, M. Recent developments in microfluidic technology for synthesis and toxicity-efficiency studies of biomedical nanomaterials. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 13, 100205.
Ferhan, A. R.; Park, S.; Park, H.; Tae, H.; Jackman, J. A.; Cho, N. J. Lipid nanoparticle technologies for nucleic acid delivery: A nanoarchitectonics perspective. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203669.
Evers, M. J. W.; Kulkarni, J. A.; Van Der Meel, R.; Cullis, P. R.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R. M. State-of-the-art design and rapid-mixing production techniques of lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1700375.
Akinc, A.; Maier, M. A.; Manoharan, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Jayaraman, M.; Barros, S.; Ansell, S.; Du, X. Y.; Hope, M. J.; Madden, T. D. et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1084–1087.
Polack, F. P.; Thomas, S. J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J. L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E. D.; Zerbini, C. et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA covid-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615.
Wei, Y. C.; Quan, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhan, Q. Q. Factors relating to the biodistribution & clearance of nanoparticles & their effects on in vivo application. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1495–1512.
Nakamura, T.; Kawai, M.; Sato, Y.; Maeki, M.; Tokeshi, M.; Harashima, H. The effect of size and charge of lipid nanoparticles prepared by microfluidic mixing on their lymph node transitivity and distribution. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2020, 17, 944–953.
Chen, S. M.; Tam, Y. Y. C.; Lin, P. J. C.; Sung, M. M. H.; Tam, Y. K.; Cullis, P. R. Influence of particle size on the in vivo potency of lipid nanoparticle formulations of siRNA. J Control Release 2016, 235, 236–244.
Prakash, G.; Shokr, A.; Willemen, N.; Bashir, S. M.; Shin, S. R.; Hassan, S. Microfluidic fabrication of lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of nucleic acids. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2022, 144, 114197.
Hirsjärvi, S.; Sancey, L.; Dufort, S.; Belloche, C.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Garcion, E.; Coll, J. L.; Hindré, F.; Benoît, J. P. Effect of particle size on the biodistribution of lipid nanocapsules: Comparison between nuclear and fluorescence imaging and counting. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 594–600.
Qi, J. P.; Zhuang, J.; Lu, Y.; Dong, X. C.; Zhao, W. L.; Wu, W. In vivo fate of lipid-based nanoparticles. Drug Discovery Today 2017, 22, 166–172.
Piwowarczyk, L.; Mlynarczyk, D. T.; Krajka-Kuzniak, V.; Majchrzak-Celinska, A.; Budzianowska, A.; Tomczak, S.; Budzianowski, J.; Wozniak-Braszak, A.; Pietrzyk, R.; Baranowski, M. et al. Natural compounds in liposomal nanoformulations of potential clinical application in glioblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 6222.
Webb, C.; Forbes, N.; Roces, C. B.; Anderluzzi, G.; Lou, G.; Abraham, S.; Ingalls, L.; Marshall, K.; Leaver, T. J.; Watts, J. A. et al. Using microfluidics for scalable manufacturing of nanomedicines from bench to GMP: A case study using protein-loaded liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119266.
Firmino, P. C. O. S.; Vianna, S. S. V.; Da Costa, O. M. M. M.; Malfatti-Gasperini, A. A.; Gobbi, A. L.; Lima, R. S.; De La Torre, L. G. 3D micromixer for nanoliposome synthesis: A promising advance in high mass productivity. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2971–2985.
Erfle, P.; Riewe, J.; Cai, S. T.; Bunjes, H.; Dietzel, A. Horseshoe lamination mixer (HLM) sets new standards in the production of monodisperse lipid nanoparticles. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 3025–3044.
Huang, P. H.; Zhao, S. G.; Bachman, H.; Nama, N.; Li, Z. S.; Chen, C. Y.; Yang, S. J.; Wu, M. X.; Zhang, S. P.; Huang, T. J. Acoustofluidic synthesis of particulate nanomaterials. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2019, 6, 1900913.
Zhao, S. G.; Huang, P. H.; Zhang, H. Y.; Rich, J.; Bachman, H.; Ye, J.; Zhang, W. F.; Chen, C. Y.; **e, Z. M.; Tian, Z. H. et al. Fabrication of tunable, high-molecular-weight polymeric nanoparticles via ultrafast acoustofluidic micromixing. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2453–2463.
Kimura, N.; Maeki, M.; Sato, Y.; Note, Y.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Harashima, H.; Tokeshi, M. Development of the iLiNP device: Fine tuning the lipid nanoparticle size within 10 nm for drug delivery. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5044–5051.
Cheung, C. C. L.; Al-Jamal, W. T. Sterically stabilized liposomes production using staggered herringbone micromixer: Effect of lipid composition and PEG-lipid content. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 687–696.
Khairnar, S. V.; Pagare, P.; Thakre, A.; Nambiar, A. R.; Junnuthula, V.; Abraham, M. C.; Kolimi, P.; Nyavanandi, D.; Dyawanapelly, S. Review on the scale-up methods for the preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1886.
Giorello, A.; Nicastro, A.; Berli, C. L. A. Microfluidic platforms for the production of nanoparticles at flow rates larger than one liter per hour. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101588.
Shepherd, S. J.; Warzecha, C. C.; Yadavali, S.; El-Mayta, R.; Alameh, M. G.; Wang, L. L.; Weissman, D.; Wilson, J. M.; Issadore, D.; Mitchell, M. J. Scalable mRNA and siRNA lipid nanoparticle production using a parallelized microfluidic device. Nano Lett 2021, 21, 5671–5680.
Han, J. Y.; La Fiandra, J. N.; DeVoe, D. L. Microfluidic vortex focusing for high throughput synthesis of size-tunable liposomes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6997.
Lim, J. M.; Swami, A.; Gilson, L. M.; Chopra, S.; Choi, S.; Wu, J.; Langer, R.; Karnik, R.; Farokhzad, O. C. Ultra-high throughput synthesis of nanoparticles with homogeneous size distribution using a coaxial turbulent jet mixer. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6056–6065.
Tomeh, M. A.; Mansor, M. H.; Hadianamrei, R.; Sun, W. Z.; Zhao, X. B. Optimization of large-scale manufacturing of biopolymeric and lipid nanoparticles using microfluidic swirl mixers. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 620, 121762.
Xu, R. C.; Tomeh, M. A.; Ye, S. Y.; Zhang, P.; Lv, S. W.; You, R. R.; Wang, N.; Zhao, X. B. Novel microfluidic swirl mixers for scalable formulation of curcumin loaded liposomes for cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 622, 121857.
Belliveau, N. M.; Huft, J.; Lin, P. J.; Chen, S. M.; Leung, A. K. K.; Leaver, T. J.; Wild, A. W.; Lee, J. B.; Taylor, R. J.; Tam, Y. K. et al. Microfluidic synthesis of highly potent limit-size lipid nanoparticles for in vivo delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2012, 1, e37.
Desai, D.; Guerrero, Y. A.; Balachandran, V.; Morton, A.; Lyon, L.; Larkin, B.; Solomon, D. E. Towards a microfluidics platform for the continuous manufacture of organic and inorganic nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 35, 102402.
Maeki, M.; Okada, Y.; Uno, S.; Sugiura, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Okuda, K.; Sato, Y.; Ando, M.; Yamazaki, H.; Takeuchi, M. et al. Mass production system for RNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles using piling up microfluidic devices. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 31, 101754.
Toth, M. J.; Kim, T.; Kim, Y. Robust manufacturing of lipid-polymer nanoparticles through feedback control of parallelized swirling microvortices. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2805–2813.
Zhang, J. S.; Wang, K.; Teixeira, A. R.; Jensen, K. F.; Luo, G. S. Design and scaling up of microchemical systems: A review. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2017, 8, 285–305.
Elvira, K. S.; I Solvas, X. C.; Wootton, R. C. R.; deMello, A. J. The past, present and potential for microfluidic reactor technology in chemical synthesis. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 905–915.
Roces, C. B.; Lou, G.; Jain, N.; Abraham, S.; Thomas, A.; Halbert, G. W.; Perrie, Y. Manufacturing considerations for the development of lipid nanoparticles using microfluidics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1095.
Kulkarni, J. A.; Tam, Y. Y. C.; Chen, S.; Tam, Y. K.; Zaifman, J.; Cullis, P. R.; Biswas, S. Rapid synthesis of lipid nanoparticles containing hydrophobic inorganic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13600–13609.
Li, S. X.; Hu, Y. Z.; Li, A.; Lin, J. H.; Hsieh, K.; Schneiderman, Z.; Zhang, P. F.; Zhu, Y. N.; Qiu, C. H.; Kokkoli, E. et al. Payload distribution and capacity of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5561.
Hamdallah, S. I.; Zoqlam, R.; Erfle, P.; Blyth, M.; Alkilany, A. M.; Dietzel, A.; Qi, S. Microfluidics for pharmaceutical nanoparticle fabrication: The truth and the myth. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119408.
Layek, A.; Mishra, G.; Sharma, A.; Spasova, M.; Dhar, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Bandyopadhyaya, R. A Generalized three-stage mechanism of ZnO nanoparticle formation in homogeneous liquid medium. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 24757–24769.
Buschmann, M. D.; Carrasco, M. J.; Alishetty, S.; Paige, M.; Alameh, M. G.; Weissman, D. Nanomaterial delivery systems for mRNA vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 65.
Wei, T.; Cheng, Q.; Min, Y. L.; Olson, E. N.; Siegwart, D. J. Systemic nanoparticle delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins for effective tissue specific genome editing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3232.
Chandler, M.; Panigaj, M.; Rolband, L. A.; Afonin, K. A. Challenges in optimizing RNA nanostructures for large-scale production and controlled therapeutic properties. Nonomedinine 2020, 75, 1331–1340.
Akinc, A.; Zumbuehl, A.; Goldberg, M.; Leshchiner, E. S.; Busini, V.; Hossain, N.; Bacallado, S. A.; Nguyen, D. N.; Fuller, J.; Alvarez, R. et al. A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 561–569.
Acknowledgements
This research work has been supported in part by Collaborative Innovation Program of Hefei Science Center, CAS (No. 2022HSC-CIP001), Anhui Province Key Laboratory of High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging (No. KFKT-2022-0003), Joint Research Fund for Overseas Chinese, Hong Kong and Macao Young Scholars (No. 51929501), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFF0705002). The authors would like to acknowledge the USTC Experimental Center of Engineering and Material Sciences and the USTC center for Micro-and Nanoscale Research and Fabrication for technical support in microfabrication. The authors would like to acknowledge Wulin Zhu for the assistance in fabrication of microfluidic chip.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_6031_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Scalable synthesis of lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid drug delivery using an isometric channel-size enlarging strategy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Tong, H., Lin, S. et al. Scalable synthesis of lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid drug delivery using an isometric channel-size enlarging strategy. Nano Res. 17, 2899–2907 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6031-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6031-1