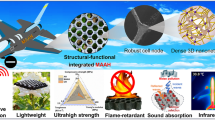
Abstract
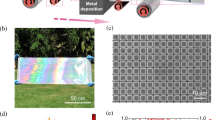
Controlling the orientation of two-dimensional MXene within layered films is essential to optimize or tune their mechanical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding (EMI) performance, but achieving the high orientation MXene layers on an industrial scale remains a challenging goal. In this paper, a scalable layer-by-layer blade coating (LbLBC) method was employed to fabricate highly oriented MXene/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) films. During the LbLBC process, MXene/PVA colloid suffered a strong shearing effect, which induced the ordered alignment of MXene nanosheets along the direction of the blade movement. The orientation of MXene can be effectively adjusted by changing the scra** gap of LbLBC, achieving a maximum Herman orientation factor f of 0.81. As a result, the mechanical properties and EMI performance of the as-prepared MXene/PVA films are in direct proportion to their orientation, with the optimal values of tensile strength of 145.5 MPa, fracture strain of 19.6%, toughness of 17.7 MJ·m−3, and EMI shielding effectiveness of 36.7 dB. Furthermore, the inherently low mid-infrared (mid-IR) emissivity of MXene, combined with the densely oriented structure affords the composite films with IR stealth, resulting in a substantial decrease from 150 to 66.1 °C in the radiative temperature of a surface. Conclusively, these scalable MXene/PVA films exhibit remarkable potential for integration into the next generation of multifunctional protective camouflage materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kolanowska, A.; Janas, D.; Herman, A. P.; Jedrysiak, R. G.; Gizewski, T.; Boncel, S. From blackness to invisibility—Carbon nanotubes role in the attenuation of and shielding from radio waves for stealth technology. Carbon 2018, 726, 31–52.
Hu, J. H.; Hu, Y.; Ye, Y. H.; Shen, R. Q. Unique applications of carbon materials in infrared stealth: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139147.
An, Z. M.; Li, Y. P.; Luo, X. G.; Huang, Y. X.; Zhang, R. B.; Fang, D. N. Multilaminate metastructure for high-temperature radar-infrared bi-stealth: Topological optimization and near-room-temperature synthesis. Matter 2022, 5, 1937–1952.
Wu, Y.; Tan, S. J.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L. L.; Zhou, M.; Ji, G. B. Broadband multispectral compatible absorbers for radar, infrared and visible stealth application. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 135, 101088.
Zhang, Y. X.; Li, L.; Cao, Y. X.; Yang, Y. Y.; Wang, W. J.; Wang, J. F. High- strength, low infrared-emission nonmetallic films for highly efficient Joule/solar heating, electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal camouflage. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 235–247.
Deng, Z. M.; Jiang, P. Z.; Wang, Z. G.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z. Z.; Zhang, H. B. Scalable production of catecholamine-densified MXene coatings for electromagnetic shielding and infrared stealth. Small 2023, 19, 2304278.
Yao, J. R.; Zhou, J. T.; Yang, F.; Peng, G. Y.; Liu, Y. J.; Yao, Z. J.; Wu, F.; Zeng, H. B. Multi-functional and multi-scenario applications for MXene aerogels with synergistically enhanced asymmetric modules. Nano Res., in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6154-4.
Liang, C. B.; Gu, Z. J.; Zhang, Y. L.; Ma, Z. L.; Qiu, H.; Gu, J. W. Structural design strategies of polymer matrix composites for electromagnetic interference shielding: A review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 181.
Song, P.; Liu, B.; Liang, C. B.; Ruan, K. P.; Qiu, H.; Ma, Z. L.; Guo, Y. Q.; Gu, J. W. Lightweight, flexible cellulose-derived carbon aerogel@reduced graphene oxide/PDMS composites with outstanding EMI shielding performances and excellent thermal conductivities. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 91.
Ma, Z. L.; Kang, S. L.; Ma, J. Z.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Liu, C.; Wei, A. J.; **ang, X. L.; Wei, L. F.; Gu, J. W. Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber-Ti3C2Tx MXene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8368–8382.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ma, Z. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Flxxible Ti3C2Tx/(aramid nanofiber/PVA) composite films for superior electromagnetic interference shielding. Resaachh 2022, 2022, 9780290.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Shi, X. T.; Qiu, H.; Pan, Y.; Yan, Y.; Gu, J. W. Ti3T2Tx/rGO porous composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding performances. Carbon 2021, 175, 271–280.
Wan, S. J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, N. N.; Wang, S. J.; Du, Y.; Xu, Z. P.; Deng, X. L.; Dou, S. X.; Jiang, L. et al. Ultrastrong MXene films via the synergy of intercalating small flakes and interfacial bridging. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7340.
Wan, H. J.; Liu, N.; Tang, J.; Wen, Q. Y.; **ao, X. Substaate-independent Ti3C2Tx MXene waterborne paint for terahertz absorption and shielding. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13646–13652.
Li, L. L.; Deng, Z. M.; Chen, M. J.; Yu, Z. Z.; Russell, T. P.; Zhang, H. B. 3D printing of ultralow-concentration 2D nanomaterial inks for multifunctional architectures. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 155–162.
Jiang, P. Z.; Deng, Z. M.; Min, P.; Ye, L. X.; Qi, C. Z.; Zhao, H. Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. B.; Yu, Z. Z. Direct ink writing of multifunctional gratings with gel-like MXene/norepinephrine ink for dynamic electromagnetic interference shielding and patterned Joule heating. Nano Res., in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6044-9.
Li, X. L.; Li, M. H.; Li, X.; Fan, X. M.; Zhi, C. Y. Low infrared emissivity and strong stealth of ti-based MXenes. Research 2022, 2022, 9892628.
Li, L.; Shi, M. K.; Liu, X. Y.; **, X. X.; Cao, Y. X.; Yang, Y. Y.; Wang, W. J.; Wang, J. F. Ultrathin titanium carbide (MXene) films for high-temperature thermal camouflage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101381.
Deng, Z. M.; Li, L. L.; Tang, P. P.; Jiao, C. Y.; Yu, Z. Z.; Koo, C. M.; Zhang, H. B. Controllable surface-grafted MXene inks for electromagnetic wave modulation and infrared anti-counterfeiting applications. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16976–16986.
Cao, W. T.; Chen, F. F.; Zhu, Y. J.; Zhang, Y. G.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Ma, M. G.; Chen, F. Binary strengthening and toughening of MXene/cellulose nanofiber composite paper with nacre-inspired structure and superior electromagnetic interference shielding properties. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4583–4593.
Wang, J.; Ma, X. Y.; Zhou, J. L.; Du, F. L.; Teng, C. Bioinspired, high-strength, and flexible MXene/aramid fiber for electromagnetic interference shielding papers with joule heating performance. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6700–6711.
**ong, J. H.; Ding, R. J.; Liu, Z. L.; Zheng, H. W.; Li, P. Y.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xue, F. H.; Peng, Q. Y. et al. High-strength, super-tough, and durable nacre-inspired MXene/heterocyclic aramid nanocomposite films for electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal management. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 171, 145972.
Zhao, B.; Ma, Z. L.; Sun, Y. Y.; Han, Y. X.; Gu, J. W. Flexible and robust Ti3C2T,/(ANF@FeNi) composite films with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding and electrothermal conversion performances. Small Struct. 2022, 3, 2200162.
Wan, Y. Z.; **ong, P. X.; Liu, J. Z.; Feng, F. F.; Xun, X. W.; Gama, F. M.; Zhang, Q. C.; Yao, F. L.; Yang, Z. W.; Luo, H. L. et al. Ultrathin, strong, and highly flexible Ti3C2Tx MXene/acterrial cellulose composite films for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8439–8449.
Luo, S. L.; **ang, T. T.; Dong, J. W.; Su, F. M.; Ji, Y. X.; Liu, C. T.; Feng, Y. Z. A double crosslinking MXene/cellulose nanofiber layered film for improving mechanical properties and stable electromagnetic interference shielding performance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 127–134.
Feng, S. Y.; Yi, Y.; Chen, B. X.; Deng, P. C.; Zhou, Z. H.; Lu, C. H. Rheology-guided assembly of a highly aligned MXene/cellulose nanofiber composite film for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding and infrared stealth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 36060–36070.
Gong, S.; Sheng, X. X.; Li, X. L.; Sheng, M. J.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.; Qu, J. P. A Multifunctional flexible composite film with excellent multi-source driven thermal management, electromagnetic interference shielding, and fire safety performance, inspired by a “brick-mortar” sandwich structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200570.
Cao, W. T.; Ma, C.; Tan, S.; Ma, M. G.; Wan, P. B.; Chen, F. Ultrathin and flexible CNTs/MXene/cellulose nanofibrils composite paper for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano- Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 72.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ma, Z. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Multifunctional Ti3C2Tx-(Fe3O4/polyimide) composite films with Janus structure for outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding and superior visual thermal management. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5601–5609.
Hu, D. W.; Wang, S. Q.; Zhang, C.; Yi, P. S.; Jiang, P. K.; Huang, X. Y. Ultrathin MXene-aramid nanofiber electromagnetic interference shielding films with tactile sensing ability withstanding harsh temperatures. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2837–2845.
Li, Y. L.; Zhou, B.; Shen, Y.; He, C. G.; Wang, B.; Liu, C. T.; Feng, Y. Z.; Shen, C. Y. Scalable manufacturing of flexible, durable Ti3C2Tx MXene/Polyvinylidene fluoride film for multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding and electro/photo-thermal conversion applications. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2021, 217, 108902.
Weng, G. M.; Li, J. Y.; Alhabeb, M.; Karpovich, C.; Wang, H.; Lipton, J.; Maleski, K.; Kong, J.; Shaulsky, E.; Elimelech, M. et al. Layer-by-layer assembly of cross-functional semi-transparent MXene-carbon nanotubes composite films for next-generation electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803360.
Chen, W.; Liu, L. X.; Zhang, H. B.; Yu, Z. Z. Flexible, transparent, and conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene-silver nanowire films with smart acoustic sensitivity for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16643–16653.
Dong, J. W.; Feng, Y. Z.; Lin, K.; Zhou, B.; Su, F. M.; Liu, C. T. A stretchable electromagnetic interference shielding fabric with dual-mode passive personal thermal management. Adv. Funct. Mater., in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202310774.
Cheng, R.; Wang, B.; Zeng, J. S.; Li, J. P.; Xu, J.; Gao, W. H.; Chen, K. F. Junus-inspired flexible cellulose nanofiber-assisted MXene/silver nanowire papers with fascinating mechanical properties for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2023, 202, 314–324.
Tang, T. T.; Wang, S. C.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Z. G.; Chen, Y.; Peng, T. S.; Khan, F.; Feng, J. B.; Song, P. A.; Zhao, Y. Flexible and flame-retarding phosphorylated MXene/polypropylene composites for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 111, 66–75.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Zhou, K.; Gu, J. W. Controlled distributed Ti3C2Tx hollow microspheres on thermally conductive polyimide composite films for excellent electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211642.
Ma, T. B.; Ma, H.; Ruan, K. P.; Shi, X. T.; Qiu, H.; Gao, S. Y.; Gu, J. W. Thermally conductive poly(lactic acid) composites with superior electromagnetic shielding performances via 3D printing technology. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 40, 248–255.
Zhou, T. X.; Zhao, C. Q.; Liu, Y. H.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H. S.; Nie, Z. D.; Fan, M.; Zhao, T. Y.; Cheng, Q. F.; Liu, M. J. Lagge-aeea ultrastrong and stiff layered MXene nanocomposites by shear-flow-induced alignment of nanosheets. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 12013–12023.
Zhang, J. Z.; Kong, N.; Uzun, S.; Levitt, A.; Seyedin, S.; Lynch, P. A.; Qin, S.; Han, M. K.; Yang, W. R.; Liu, J. Q. et al. Scalable manufacturing of free-standing, strong Ti3C2Tx MXene films with outstanding conductivity. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001093.
Yu, J.; Cheng, H. L.; Wang, Y.; He, C. G.; Zhou, B.; Liu, C. T.; Feng, Y. Z. Multiple shearing-induced high alignment in polyethylene/graphene films for enhancing thermal conductivity and solar-thermal conversion performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148062.
Ling, Z.; Ren, C. E.; Zhao, M. Q.; Yang, J.; Giammarco, J. M.; Qiu, J. S.; Barsoum, M. W.; Gogotsi, Y. Flexible and conductive MXene films and nanocomposites with high capacitance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16676–16681.
Zheng, J. L.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y. L.; Wu, F. Z.; Wang, W. H.; Wang, H.; Sun, S. Y.; Lu, J. Paraffin/polyvinyl alcohol/MXene flexible phase change composite films for thermal management applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139727.
Wang, B. B.; Jia, P. F.; Zhang, Y.; He, R. F.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Multifunctional composite polyvinyl alcohol films prepared with economic conductive carbon black and MXene microcapsuled APP. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 30, 100928.
Zhang, Y.; Xu, M. K.; Wang, Z. G.; Zhao, T. Y.; Liu, L. X.; Zhang, H. B.; Yu, Z. Z. Strong and conductive reduced graphene oxide-MXene porous films for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4916–4924.
Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. L.; Han, G. J.; Feng, Y. Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D. B.; Ma, J. M.; Liu, C. T. Flexible, robust, and multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding film with alternating cellulose nanofiber and MXene layers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4895–4905.
Luo, S. L.; Li, Q.; Xue, Y. J.; Zhou, B.; Feng, Y. Z.; Liu, C. T. Reinforcing and toughening bacterial cellulose/MXene films assisted by interfacial multiple cross-linking for electromagnetic interference shielding and photothermal response. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 652, 1645–1652.
Han, G. J.; Zhou, B.; Li, Z. Y.; Feng, Y. Z.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. Ultrafine aramid nanofibers prepared by high-efficiency wet ball-milling-assisted deprotonation for high-performance nanopaper. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 3051–3060.
Luo, S. H.; Patole, S.; Anwer, S.; Li, B. S.; Delclos, T.; Gogotsi, O.; Zahorodna, V.; Balitskyi, V.; Liao, K. Tensile behaviors of Ti3C2Tx (MXene) films. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 395704.
Peng, M. Y.; Qin, F. X. Clarification of basic concepts for electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 225108.
Feng, Y. Z.; Song, J. Z.; Han, G. J.; Zhou, B.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. Transparent and stretchable electromagnetic interference shielding film with fence-like aligned silver nanowire conductive network. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2201490.
Li, R. S.; Ding, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, H. M.; Zeng, D.; Zhao, B.; Fan, B. B.; Zhang, R. Tuning of anisotropic electrical conductivity and enhancement of EMI shielding of polymer composite foam via CO2-assisted delamination and orientation of MXene. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128930.
Rajavel, K.; Luo, S. B.; Wan, Y. J.; Yu, X. C.; Hu, Y. G.; Zhu, P. L.; Sun, R.; Wong, C. 2D Ti3C2T MXene/polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanocomposites for attenuation of electromagnetic radiation with excellent heat dissipation. Compos. Part A: Appls. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 129, 105693.
Xu, H. L.; Yin, X. W.; Li, X. L.; Li, M. H.; Liang, S.; Zhang, L. T.; Cheng, L. F. Lightweight Ti2CT MXene/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite foams for electromagnetic wave shielding with absorption-dominated feature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10198–10207.
Liu, F.; Li, Y. C.; Hao, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhan, Y. H.; Zhang, C. M.; Meng, Y. Y.; **e, Q.; **a, H. S. Well-aligned MXene/chitosan films with humidity response for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 243, 116467.
Liu, H. G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. J.; Wu, S. Q.; Wang, C. K.; You, C. Y.; Tian, N. Thermally conductive MWCNTs/Fe3O4/Ti3C2Tx MXene multi-layer films for broadband electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 75–85.
Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Sang, M.; Zhou, J. Y.; Zhang, J. S.; Xuan, S. H.; Gong, X. L. Nacre- mimetic hierarchical architecture in polyborosiloxane composites for synergistically enhanced impact resistance and ultra-efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19067–19086.
Lv, D. D.; Fang, N.; Zhang, W. G. A PDMS modified polyurethane/Ag composite coating with super-hydrophobicity and low infrared emissivity. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 108, 103351.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support for this work by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52273085, 52303113, and 12072325), the Natural Science Foundation of China of Henan Province (No. 222300420541), and the Key Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province, China (No. 24A430045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2024_6486_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Highly oriented MXene/polyvinyl alcohol films prepared by scalable layer-by-layer blade coating for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and infrared stealth
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, J., Li, Z., Liu, C. et al. Highly oriented MXene/polyvinyl alcohol films prepared by scalable layer-by-layer blade coating for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and infrared stealth. Nano Res. 17, 5651–5660 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6486-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6486-8