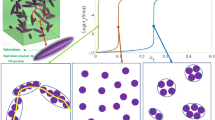
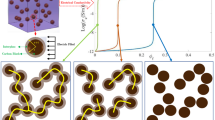
Abstract
In this work, the electrical conductivity of nanocomposites filled with carbon black is simulated by the three-dimensional Monte Carlo method. First, three-dimensional model of the nanocomposites and carbon black is constructed and the conductive mechanism is studied. Then the calculation method of electrical conductivity of nanocomposites filled with carbon black is proposed according to the equivalent resistance of large-scale pure resistor network. Then the proposed electrical conductivity calculation method is verified by comparing with the simulation and experimental results. This result shows that it is feasible to directly obtain the conductivity of nanocomposites using the proposed conductivity calculation method. This study helps to estimate the electrical properties of nanocomposites filled with carbon black. And it also can help for studying nanocomposites filled with carbon nanotubes or graphene and the synergistic effect of hybrid fillers-filled nanocomposites.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
X. H. Guo, Y. Huang, Y. N. Zhao, L. D. Mao, L. Gao, W. D. Pan, Y. G. Zhang, and P. Liu, Smart Mater. Struct. 26, 095017 (2017).
F. Wang, S. Liu, L. Shu, and X. M. Tao, Carbon 121, 353 (2017).
W. Zhai, Q. J. **a, K. K. Zhou, X. Y. Yue, M. N. Ren, G. Q. Zheng, K. Dai, C. T. Liu, and C.Y. Shen, Chem. Eng. J. 372, 373 (2019).
X. T. Chang, S. H. Sun, S. B. Sun, T. Liu, X. **ong, Y. H. Lei, L. H. Dong, and Y. S. Yin, J. Alloys Compd. 738, 111 (2018).
K. Y. Huang, H. M. Ning, N. Hu, X. P. Wu, S. Wang, S. Y. Weng, W. F. Yuan, Alamusi, L. K. Wu, and Y. L. Liu, Carbon 144, 509 (2019).
D. F. Wu, Q. L. Lv, S. H. Feng, J. X. Chen, Y. Chen, Y. X. Qiu, and X. Yao, Carbon 95, 380 (2015).
M. Wen, X. J. Sun, L. Su, J. B. Shen, J. Li, and S. Y. Guo, Polymer 53, 1602 (2012).
S. Chatterjee, F. Nafezarefi, N. H. Tai, L. Schlagenhauf, F. A. Nuesch, and B. T. T. Chu, Carbon 50, 5380 (2012).
K. H. Nam, J. Yu, N. H. You, H. Han, and B. C. Ku, Compos. Sci. Technol. 149, 228 (2017).
F. Lux, J. Mater. Sci. 28, 285 (1993).
Y. Huang, W. D. Wang, X. Zeng, X. H. Guo, Y. Y. Zhang, P. Liu, Y. M. Ma, and Y. G. Zhang, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 135, 46517 (2018).
Y. L. Chen, S. T. Wang, F. Pan, and J. Y. Zhang, J. Nanomater. 2014, 614797 (2014).
R. L. V. Wal, A. J. Tomasek, Combust. Flame 136, 129 (2004).
X. J. Ni, C. Hui, N. H. Su, W. Jiang, and F. Liu, Nanotechnology 29, 075401 (2017).
C. Fang, J. J. Zhang, X. Q. Chen, and G. J. Weng, Carbon 146, 125 (2019).
G. Ambrosetti, C. Grimaldi, I. Balberg, T. Maeder, A. Danani, and P. Ryser, Phys. Rev. B: Condesn. Matter Mater. Phys. 81, 155434 (2010).
Y. L. Chen, F. Pan, S. T. Wang, B. Liu, and J. Y. Zhang, Compos. Struct. 124, 292 (2015).
I. Balberg, Carbon 40, 139 (2002).
M. Sumita, K. Sakata, S. Asai, K. Miyasaka, and H. Nakagawa, Polym. Bull. 25, 265 (1991).
T. Mondal, A. K. Bhowmick, R. Ghosal, and R. Mukhopadhyay, Polymer 146, 31 (2018).
P. Raut, N. Swanson, A. Kulkarni, C. Pugh, and S. C. Jana, Polymer 148, 247 (2018).
F. Panozzo, M. Zappalorto, and M. Quaresimin, Composites, Part B 109, 53 (2017).
I. Balberg, N. Wagner, Y. Goldstein, and S. Z. Weisz, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 195, 233 (1990).
E. K. Sichel, J. I. Gittleman, and P. Sheng, Phys. Rev. B: Solid State 18, 5712 (1978).
P. Sheng, E. K. Sichel, and J. I. Gittleman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 40, 1197 (1978).
G. R. Ruschau, S. Yoshikawa, and R. E. Newnham, J. Appl. Phys.72, 953 (1992).
D. Pantea, H. Darmstadt, S. Kaliaguine, L. Summchen, and C. Roy, Carbon 39, 1147 (2001).
B. Marinho, M. Ghislandi, E. Tkalya, C. E. Koning, and G. de With, Powder Technol. 221, 351 (2012).
E. Laredo, M. Grimau, A. Bello, D. F. Wu, Y. S. Zhang, and D. P. Lin, Biomacromolecules 11, 1339 (2010).
A. B. Oskouyi, U. Sundararaj, and P. Mertiny, Materials 7, 2501 (2014).
A. Allaoui, S. V. Hoa, and M. D. Pugh, Compos. Sci. Technol. 68, 410 (2008).
I. Balberg, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 1305 (1987).
S. Maiti, and B. B. Khatua, Polym. Compos. 37, 2058 (2015).
N. Johner, C. Grimaldi, I. Balberg, and P. Ryser, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 77, 174204 (2008).
M. Q. Owaidat, J. H. Asad, and Z. Z. Tan, Results Phys. 12, 1621 (2019).
J. Cserti, G. Szechenyi, and G. David, J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 44, 215201 (2011).
H. M. Ma, and X. L. Gao, Polymer 49, 4230 (2008).
Y. Benveniste, Mech. Mater. 6, 147 (1987).
S. H. Park, J. Hwang, G. S. Park, J. H. Ha, M. Zhang, D. Kim, D. J. Yun, S. Lee and S. H. Lee, Nat. Commun. 10, 2537 (2019).
D. S. McLachlan, M. Blaszkiewicz, and R. E. Newnham, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 2187 (1990).
Funding
This work was supported by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (Grant no. JZ2020HGTB0027), funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 61401141, 91648206, 61471155, and 61673369), funded from Key Research and Development Project of Zhejiang Province (Grant no. 2018C01041), and Hefei University of Technology’s Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates (Grant no. 201910359075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiawen Ji, **a, P., Zhu, X. et al. A Simulation for the Electrical Conductivity of Nanocomposites Filled with Carbon Black Based on the Three-dimensional Monte Carlo Method. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 63, 196–207 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X21020048
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X21020048